Atorvastatin: Why Am I Getting Muscle Pain, Diarrhea, or Fatigue?
Atorvastatin is a prescription medication used to lower “bad” cholesterol and triglycerides (fats) in the blood, usually along with a healthy diet. By reducing these fats, it helps keep blood vessels from getting clogged, which lowers the risk of serious problems like chest pain, heart attacks, and strokes. It is also often prescribed to people who have risk factors for heart disease, even if they have not yet had heart problems.
Many people search for answers like “Why do I have muscle pain or feel tired on atorvastatin?” This page uses real‑world safety data to help frame that discussion with your doctort.
This drug belongs to a group of medicines called statins. It works by blocking a substance the body uses to make cholesterol, which leads to lower cholesterol levels in the blood. Because of its proven benefits, atorvastatin has become extremely common. In 2023, Atorcastatin had 115,271,514 prescriptions and 30,675 adverse event reports filed, equivalent to a 0.027% reporting rate relative to prescriptions (Source: MeMeds Side Effects Analysis).
Like all medicines, atorvastatin has both benefits and risks, and the decision to use it should be made together with a doctor. Certain health conditions can increase the chance of side effects, so it’s important to tell your doctor if you have issues such as diabetes, thyroid problems, liver disease, heavy alcohol use, kidney disease, severe infections, or a history of seizures. It is also important to monitor blood sugar levels while taking this medication, especially for people with diabetes or those at risk. People with serious liver disease should not take this medicine, and those who recently had a stroke or a “mini-stroke” (TIA) may need extra caution.
Is Atorvastatin Safe for Me?
Key Safety Considerations
Insufficient data, consult a doctor
Use in children needs close monitoring
Dose adjustment or close monitoring in elderly
Avoid or limit alcohol consumption
May increase heart rate/jitteriness; consider limiting
Avoid grapefruit/grapefruit juice/citrus
No reported interaction
Some foods affect this medicine; follow timing/food advice
May affect alertness and coordination; use caution
Real‑World Atorvastatin Side Effects: Muscle Injury, Kidney Issues, Fatigue & More
If you’re wondering whether your muscle pain, dark urine, diarrhea, or higher blood sugar could be related to atorvastatin, these FDA reports show how often people actually report these problems.
Trend of Reported Side Effects
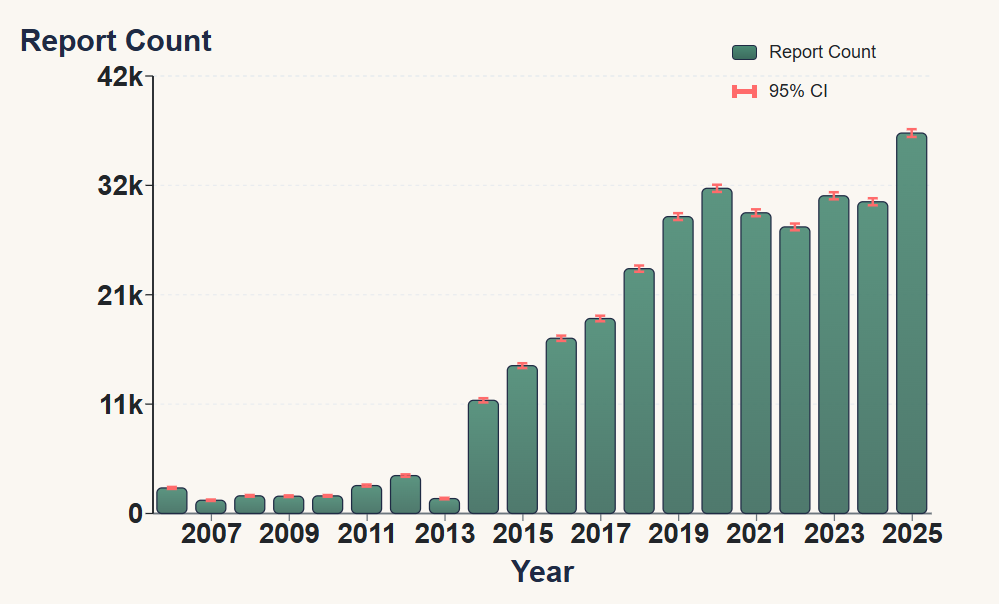
Visualization showing the trend of reported atorvastatin side effects from 2006 to 2025 based on FDA database analysis.
Total Reports Analyzed
315,469 reports over 20 years
15,773 average yearly report
Demographic Distribution
151,032 female cases
141,844 male cases
Peak reports:
60-79 age range
Data Source & Updates
FDA Database
Updated: Jan 27, 2026
95% confidence intervals applied
Most Frequently Reported Everyday Side Effects
*Report counts reflect frequency of reporting, not severity or causality.
Critical Safety Warnings
- Muscle injury risk: myopathy and rhabdomyolysis (3,964 cases)
- Liver safety: liver injury risk; caution with alcohol use
- Kidney complications: acute kidney injury (10,671 cases)
- Blood sugar effects: increased glucose (3,706 cases)
- Drug & food interactions: Grapefruit juice & interacting meds
Serious Muscle & Kidney Injury
3,964 rhabdomyolysis reports
Seek medical help for unexplained muscle pain, weakness, fever, or dark urine. Severe muscle injury may lead to kidney failure, particularly in older adults or those with underlying illness or drug interactions.
Common Real‑World Questions About Atorvastatin
Why do I still have muscle pain even after my doctor says atorvastatin is safe?
Muscle aches on atorvastatin are often mild and have many possible causes, but safety databases still record thousands of reports of myalgia and rhabdomyolysis. Use this data as a prompt for a detailed review with your doctor rather than stopping the medicine on your own.
Why are serious muscle problems reported if atorvastatin is widely prescribed?
Although serious muscle injury is considered uncommon, FDA data include 3,964 reports of rhabdomyolysis and thousands of reports of muscle pain, weakness, and spasms. These numbers reflect long-term national reporting across millions of users. Risk is higher in older adults, people with kidney disease, severe infections, thyroid disorders, or when interacting drugs are used.
What does it mean if atorvastatin seems “not working” or “ineffective” (14,582 reports)?
“Drug ineffective” does not mean atorvastatin doesn’t work. It usually reflects real-world situations such as: 1) cholesterol levels not improving enough, 2) incorrect dosing, 3) poor adherence, 4) dietary factors, or 5) disease progression requiring combination therapy. It represents treatment challenges, not failure of the drug itself.
Why are kidney problems reported with a cholesterol medicine?
Atorvastatin itself does not directly damage the kidneys in most people. However, severe muscle injury (rhabdomyolysis) can release muscle breakdown products into the blood, which can harm the kidneys. This explains why FDA data shows 10,671 reports of acute kidney injury and 5,308 reports of renal failure, often linked to severe muscle reactions.
Does atorvastatin affect blood sugar?
Yes. Real-world data includes 3,706 reports of increased blood glucose. Statins can slightly raise blood sugar levels in some people, especially those with diabetes or pre-diabetes. This is why regular blood sugar monitoring is recommended during treatment.
How does MeMeds analysis complement Mayo Clinic guidance?
Mayo Clinic provides clinical guidance based on trials and medical evidence. MeMeds analyzes data from regularoty entities (such as FDA) and scientific evidence which adds real-world insight into how side effects actually appear across large populations. For example, while guidelines mention muscle and liver risks, real-world reports show high frequencies of fatigue (18,707), diarrhea (16,589), nausea (15,544), dizziness (12,955), and myalgia (8,955), helping identify practical risk patterns.
Access real-world side effect data across 100M+ data points
Go beyond summary statistics. Use the MeMeds app to explore interactive charts, filter by demographics, compare side effect frequencies, and make data-informed decisions about your health.
Dive Deeper with MeMeds Interactive Analysis
The static data above shows only the surface. In the MeMeds app, you can explore:
- Interactive Age Distribution - See exact case counts for age group
- Annual Trend Analysis - Track reporting patterns
- Complete Side Effect List - Access up to 100 reported effects
- Real-time Updates - Get the latest data as it's processed
MeMeds transforms raw scientific and regulatory data into actionable insights personalized for your situation.
📋 Important Data Interpretation Notes
Database Limitations: These reports come from regulatory reporting system and may
over-represent adverse events. Report counts don't equal incidence rates.
Medical Context Required: This data should be discussed with healthcare providers who
can interpret it in the context of your individual health situation.
Not Medical Advice: This analysis is for informational purposes only. Always follow
your doctor's prescribed treatment plan.
Article Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and does not provide medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting or changing any medication.